In this digital era, businesses and organizations are inundated with a deluge of data from various sources. With the exponential growth in data, the challenge is no longer just about collection but about understanding, organizing, and efficiently using that data. This is where data catalogs come into play.
Acting as a comprehensive inventory for an organization’s data assets, data catalogs facilitate easy access, understanding, and governance of large datasets.
What are data catalogs?
A data catalog is a central repository where information about data is stored. It is not merely a storage space but an intricate system that indexes and organizes data in a manner that is easily accessible to users. Imagine a vast library, and think of a data catalog as the catalog system that helps you locate the exact book you are looking for, provides a summary of its content, and even offers suggestions for related reads.
Why are data catalogs crucial for businesses?
- Facilitating data discovery: With vast amounts of data scattered across various databases, spreadsheets, and systems, finding the right piece of data can be like searching for a needle in a haystack. Data catalogs simplify this process by providing users with a central location where they can search for, access, and analyze data.
- Improving collaboration: Often, different departments within an organization will have their own sets of data, leading to silos. A data catalog centralizes this data, allowing for improved collaboration and more cohesive decision-making.
- Ensuring data quality: Data catalogs often come with features that allow for the monitoring and reporting of data quality. This ensures that the data being used is accurate, up-to-date, and reliable.
- Enhancing data lineage: Understanding the source and journey of your data, often referred to as data lineage, is pivotal in ensuring transparency and trust. A data catalog offers a visual representation of data lineage, tracking its journey from source to end-use.
How do data catalogs work?
At their core, data catalogs utilize metadata to organize and classify data. Metadata is, essentially, data about data. It provides context, meaning, and structure to raw data, transforming it into something understandable and usable.
- Metadata collection: The data catalog scans various data sources, collecting metadata that provides detailed information about the source, structure, and content of the data.
- Data classification: Once collected, the metadata is classified and organized into categories, making it easy for users to search for and locate the relevant data.
- Data indexing: Like the index of a book, the data catalog indexes metadata, ensuring efficient and rapid data retrieval.
- Integration with a metadata management tool: For a more holistic approach to data management, data catalogs can be integrated with a metadata management tool. This tool manages, controls, and analyzes metadata, offering deeper insights and further enhancing the capabilities of the data catalog.
Implementing a data catalog: Best practices
- Involve all stakeholders: A data catalog’s effectiveness depends on its adoption across the organization. Engage with stakeholders from various departments to understand their needs and ensure the catalog addresses them.
- Prioritize data governance: Establish clear data governance policies to determine who can access and modify data, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Regularly update the catalog: As new data sources emerge, it is crucial to keep the catalog updated. Regular updates ensure that the catalog remains a relevant and reliable resource.
- Train your team: Implement training sessions for your team to familiarize them with the catalog’s functionalities, ensuring they can make the most out of this resource.
Enhancing User Experience with Data Catalogs
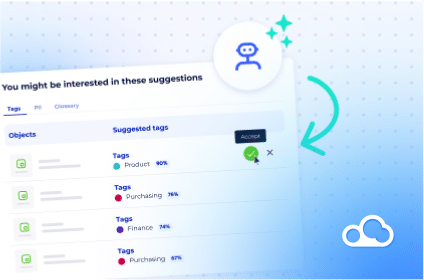
- Personalized data access: Modern data catalogs are designed to offer personalized experiences. By learning user preferences and patterns over time, they can recommend relevant datasets, much like how streaming services suggest movies or series. This can significantly reduce the time users spend searching for data, allowing them to focus on analysis and interpretation.
- Interoperability with other systems: A good data catalog is not an isolated system. It should be interoperable with other systems in an organization’s IT landscape, such as BI tools, cloud platforms, and data warehouses. This ensures a seamless flow of information, optimizing the data processing pipeline.
- Augmented data classification with AI: With the integration of artificial intelligence, data catalogs can automatically classify and tag data. For example, a data catalog can identify sensitive information and tag it for restricted access, ensuring better compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Enhanced data security: As data breaches become increasingly common and costly, the importance of securing data cannot be overstated. Advanced data catalogs come with robust security features, offering multiple layers of protection, including encryption, role-based access controls, and activity monitoring. This ensures that data is not only easily accessible to those who need it but also protected from potential threats.
With these enhancements, data catalogs not only serve as a repository and organizational tool but also evolve into intelligent systems, driving efficiency and fostering innovation in a data-driven ecosystem.
Advancing capabilities of data catalogs
- Visual data profiling: One of the emerging features in advanced data catalogs is visual data profiling. This tool provides a visual representation of the data’s statistical attributes, like distributions, outliers, and patterns. By presenting data in a more visual format, users can gain insights at a glance, making it easier to understand the nuances of the data they are working with.
- Automated data quality checks: Quality is paramount when it comes to data-driven decision-making. Future-forward data catalogs are introducing automated data quality checks, which scan the data for inconsistencies, duplicates, and errors. By identifying and highlighting these issues proactively, these catalogs help ensure that the data used for analytics and other processes is of the highest caliber.
- Feedback & collaboration tools: To foster a culture of continuous improvement, modern data catalogs are integrating feedback mechanisms. Users can rate datasets, leave comments, and even collaborate in real-time with their colleagues. This kind of interactivity promotes a more communal approach to data management, where insights and knowledge are shared, enriching the overall data experience for everyone involved.
Conclusion
With the growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making, the role of data catalogs is set to evolve. Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will be integrated to automate metadata collection, improve data classification, and offer predictive insights. As data continues to be a pivotal asset, harnessing its power efficiently and ethically will depend on tools like data catalogs.
As data continues to shape our future, the tools we use to manage and understand this data become increasingly critical. Data catalogs, with their ability to organize, streamline, and enhance our data journeys, will undoubtedly play a central role in our data-driven futures.
—
Do you still have questions about data governance? Turn to DataGalaxy to create your company’s data lineage mapping, develop a standardized business glossary, and much more! Check our calendar and select a date that works for you. Request a demo to jumpstart your free 15-day platform trial access & start making the most of your data today!